1.16. Cube Extraction  ¶
¶
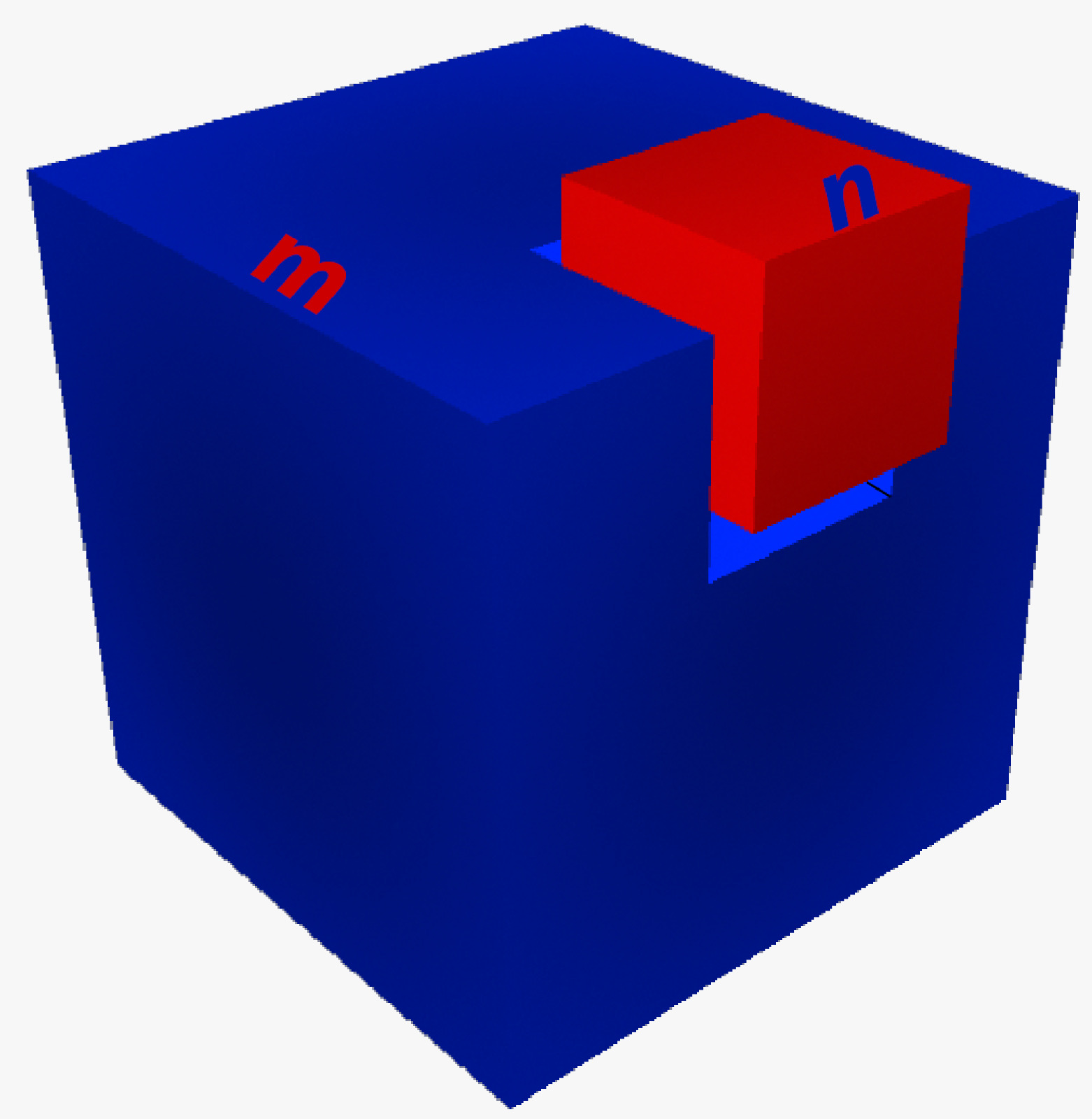
Suppose that a cube with an edge length of n is extracted from a larger cube with an edge length of m as shown in the figure above. Notice that the vertices of these two cubes do not overlap and they have only one intersecting edge.
Then the new shape after extraction of the smaller cube looks like following:
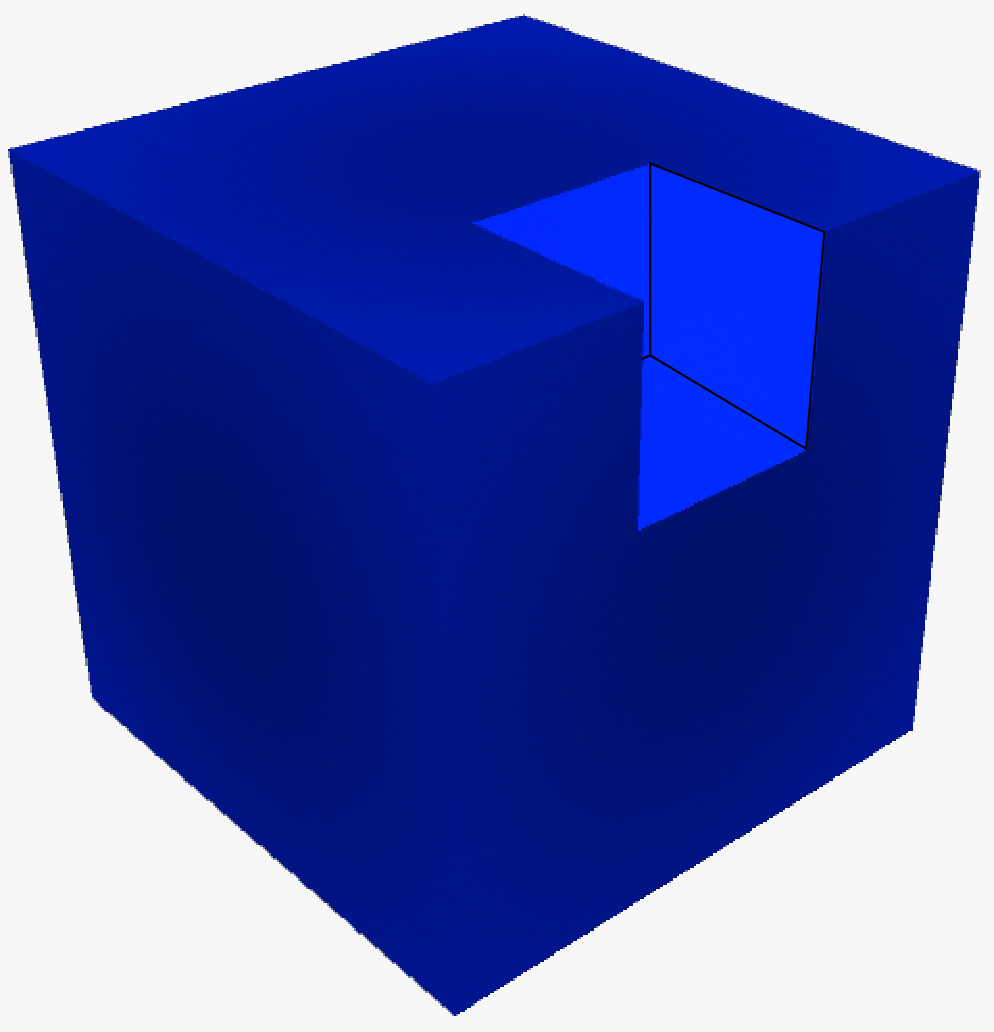
Write a program that outputs the total surface area of this new shape as an integer.
Inputs of your program will be given as integers in the following order:
m: as the edge length of the larger cube
n: as the edge length of the extracted cube
Sample I/O:
Input:
6
2
Output:
224
Input:
4
1
Output:
98
m = int(input())
n = int(input())
# extracting the smaller cube adds 2 new surface areas to the total surface area of original cube.
res = (m**2)*6 + (n**2)*2
print(res)